During the Project Execution Phase, the team implements tasks outlined in the Project Plan, focusing on coordination, quality assurance, resource management, and stakeholder updates. Also known as the implementation phase, it demands meticulous oversight from the project manager to ensure adherence to schedules and objectives. Project management software aids in task assignment, resource allocation, team communication, and streamlining processes.
Documentation such as Quality Assurance reports, meeting minutes and Work Orders are generated to track progress and maintain accountability. This phase is pivotal for achieving project goals in earlier stages, emphasizing efficient collaboration and utilization of project management tools for successful project delivery.
You’ll also likely discover new information that requires revisiting and updating the initial project management plans. Be vigilant with change requests and ensure that the necessary adjustments are made.
This phase involves implementing the project plan, coordinating resources, monitoring progress, and managing any changes or issues that may arise. Here are the key steps and activities involved in the project execution phase:
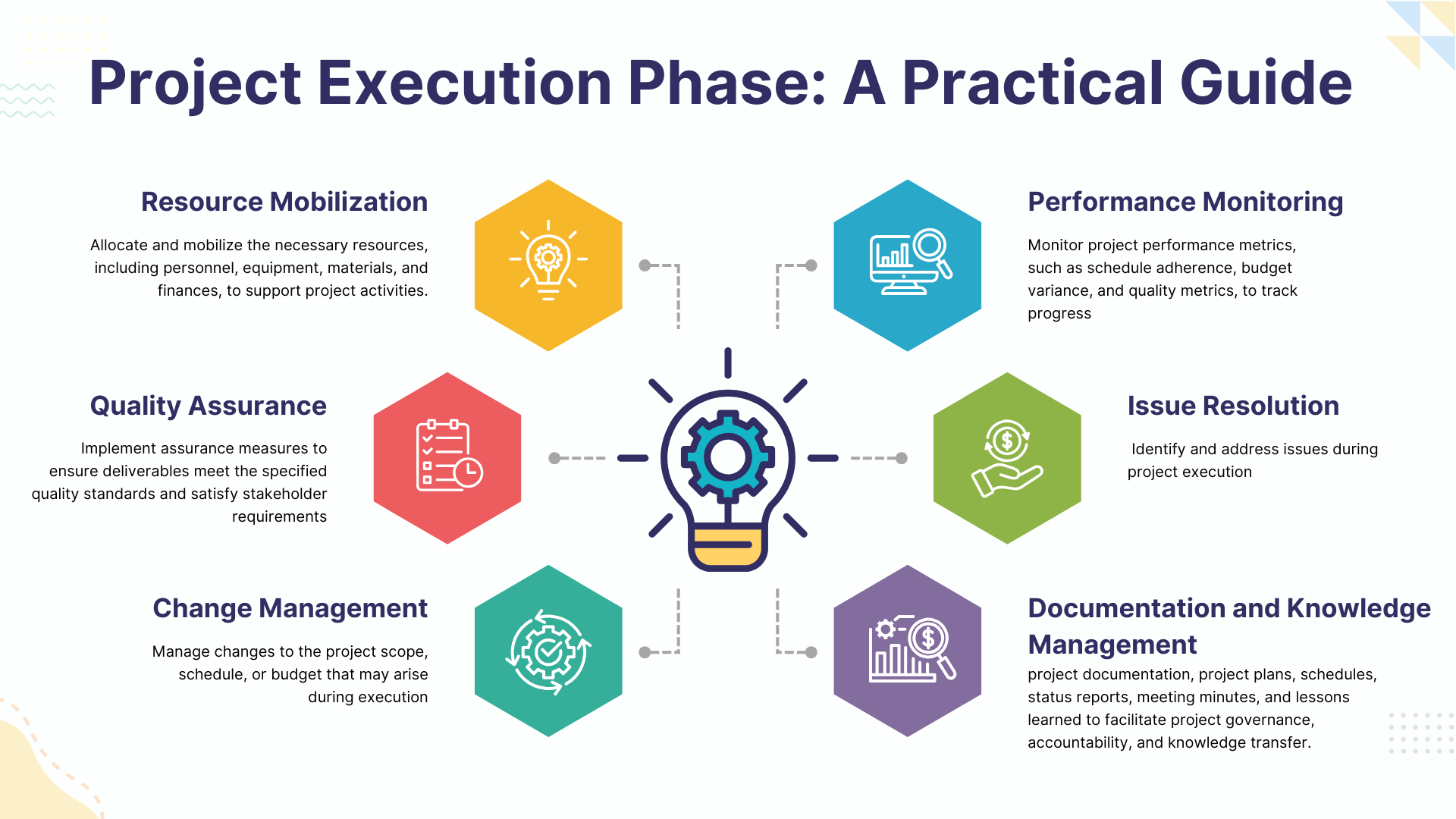
- Resource Mobilization: Allocate and mobilize the necessary resources, including personnel, equipment, materials, and finances, to support project activities.
- Task Execution: Execute the tasks and activities outlined in the project plan according to the defined schedule, scope, and quality standards. This involves coordinating and collaborating with team members, stakeholders, and vendors to complete deliverables on time and within budget.
- Quality Assurance: Implement assurance measures to ensure deliverables meet the specified quality standards and satisfy stakeholder requirements. This may involve conducting inspections, reviews, and tests to identify and address defects from the quality criteria.
- Risk Management: Monitor and manage project risks throughout the execution phase, implementing risk mitigation strategies to minimize potential threats’ impact and capitalize on opportunities. This includes regularly assessing and updating the project risk register and contingency plans.
- Communication and Reporting: Maintain regular communication, address concerns, and solicit feedback. This may involve holding status meetings, distributing progress reports, and using project management tools to facilitate collaboration and information sharing.
- Change Management: Manage changes to the project scope, schedule, or budget that may arise during execution, ensuring that all changes are appropriately documented, evaluated for their impact, and approved by the appropriate stakeholders before implementation.
- Issue Resolution: Identify and address issues during project execution, working collaboratively with team members and stakeholders to find timely and effective solutions.
- Procurement Management (if applicable): Manage procurement activities, including vendor selection, contract negotiation, and vendor performance evaluation, to ensure that project requirements and contractual obligations procure goods and services.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor project performance metrics, such as schedule adherence, budget variance, and quality metrics, to track progress that goes against the project plan and identify areas for improvement.
- Documentation and Knowledge Management: This is a process to keep project documentation, project plans, schedules, status reports, meeting minutes, and lessons learned to facilitate project governance, accountability, and knowledge transfer.
- Celebration and Recognition: To boost team morale and motivation, recognize and celebrate milestones and achievements reached during the project execution phase.
The project execution phase is characterized by active implementation, monitoring, and control activities to achieve project objectives efficiently and effectively. Effective leadership, communication, and stakeholder collaboration must ensure successful project delivery.